United States
Charting the Rise of America’s Debt Ceiling
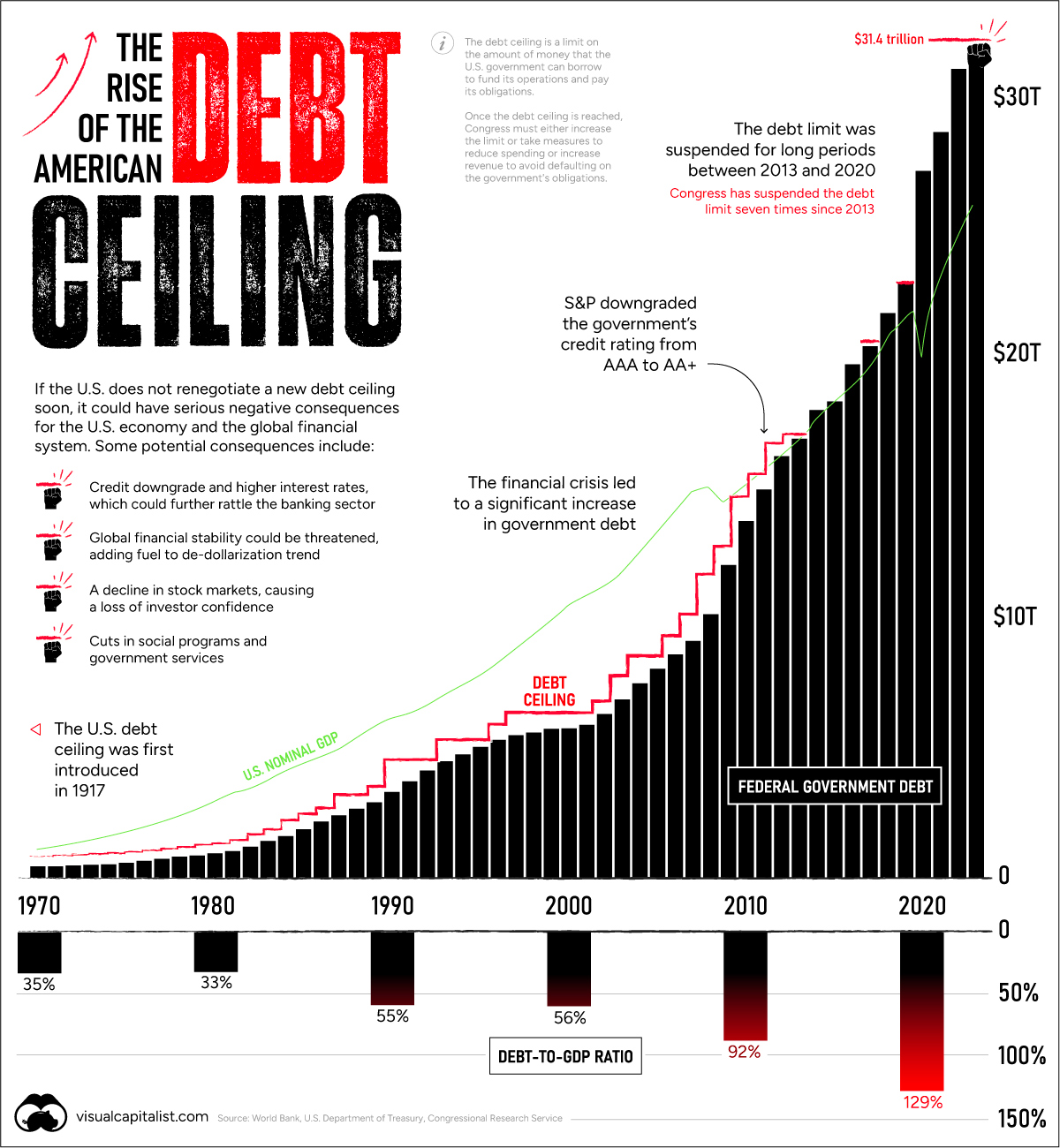
Charting the Rise of America’s Debt Ceiling
Every few years the debt ceiling standoff puts the credit of the U.S. at risk.
In January, the $31.4 trillion debt limit—the amount of debt the U.S. government can hold—was reached. That means U.S. cash reserves could be exhausted by June 1 according to Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen. Should Republicans and Democrats fail to act, the U.S. could default on its debt, causing harmful effects across the financial system.
The above graphic shows the sharp rise in the debt ceiling in recent years, pulling data from various sources including the World Bank, U.S. Department of Treasury, and Congressional Research Service.
Familiar Territory
Raising the debt ceiling is nothing new. Since 1960, it’s been raised 78 times.
In the 2023 version of the debate, Republican House Majority Leader Kevin McCarthy is asking for cuts in government spending. However, President Joe Biden argues that the debt ceiling should be increased without any strings attached. Adding to this, the sharp uptick in interest rates have been a clear reminder that rising debt levels can be precarious.
Consider that historically, interest payments on the U.S. debt have been equal to about half the cost of defense. More recently, however, the cost of servicing the debt has risen, and is now almost on par with the defense budget as a whole.
Key Moments In Recent History
Over history, raising the debt ceiling has often been a typical process for Congress.
Unlike today, agreements to raise the debt ceiling were often negotiated faster. Increased political polarization over recent years has contributed to standoffs with damaging consequences.
For instance, in 2011, an agreement was made just days before the deadline. As a result, S&P downgraded the U.S. credit rating from AAA to AA+ for the first time ever. This delay cost an estimated $1.3 billion in extra costs to the government that year.
Before then, the government shut down twice between 1995 and 1996 as President Bill Clinton and Republican House Speaker Newt Gingrich went head-to-head. Over a million government workers were furloughed for a week in late November 1995 before the debt limit was raised.
What Happens Now?
Today, Republicans and Democrats have less than two weeks to reach an agreement.
If Congress doesn’t make a deal the result would be that the government can’t pay its bills by taking on new debt. Payment for federal workers would be suspended, certain pension payments would get stalled, and interest payments on Treasuries would be delayed. The U.S. would default under these conditions.
Three Potential Consequences
Here are some of the potential knock-on effects if the debt ceiling isn’t raised by June 1, 2023:
1. Higher Interest Rates
Typically investors require higher interest payments as the risk of their debt holdings increase.
If the U.S. fails to pay interest payments on its debt and gets a credit downgrade, these interest payments would likely rise higher. This would impact the U.S. government’s interest payments and the cost of borrowing for businesses and households.
High interest rates can slow economic growth since it disincentivizes spending and taking on new debt. We can see in the chart below that a gloomier economic picture has already been anticipated, showing its highest probability since 1983.

Historically, recessions have increased U.S. deficit spending as tax receipts fall and there is less income to help fund government activities. Additional fiscal stimulus spending can also exacerbate any budget imbalance.
Finally, higher interest rates could spell more trouble for the banking sector, which is already on edge after the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank.
A rise in interest rates would push down the value of outstanding bonds, which banks hold as capital reserves. This makes it even more challenging to cover deposits, which could further increase uncertainty in the banking industry.
2. Eroding International Credibility
As the world’s reserve currency, any default on U.S. Treasuries would rattle global markets.
If its role as an ultra safe asset is undermined, a chain reaction of negative consequences could spread throughout the global financial system. Often Treasuries are held as collateral. If these debt payments fail to get paid to investors, prices would plummet, demand could crater, and global investors may shift investment elsewhere.
Investors are factoring in the risk of the U.S. not paying its bondholders.
As we can see this in the chart below, U.S. one-year credit default swap (CDS) spreads are much higher than other nations. These CDS instruments, quoted in spreads, offer insurance in the event that the U.S. defaults. The wider the spread, the greater the expected risk that the bondholder won’t be paid.
The US now has higher credit risk than Mexico, Greece, and Brazil pic.twitter.com/je4klBvHZ6
— Genevieve Roch-Decter, CFA (@GRDecter) May 11, 2023
Additionally, a default could add fuel to the perception of global de-dollarization. Since 2001, the USD has slipped from 73% to 58% of global reserves.
Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine led to steep financial sanctions, China and India are increasingly using their currencies for trade settlement. President of Russia Vladimir Putin says that two-thirds of trade is settled in yuan or roubles. Recently, China has also entered non-dollar agreements with Brazil and Kazakhstan.
3. Financial Sector Turmoil
Back at home, a debt default would hurt investor confidence in the U.S. economy. Coupled with already higher interest rates impacting costs, financial markets could see added strain. Lower investor demand could depress stock prices.
Is the Debt Ceiling Concept Flawed?
Today, U.S. government debt stands at 129% of GDP.
The annualized cost of servicing this debt has jumped an estimated 90% compared to 2011, driven by increasing debt and higher interest rates.
Some economists argue that the debt ceiling helps keep the government more fiscally responsible. Others suggest that it’s structured poorly, and that if the government approves a level of spending in its budget, that debt ceiling increases should come more automatically.
In fact, it’s worth noting that the U.S. is one of the few countries worldwide with a debt ceiling.
United States
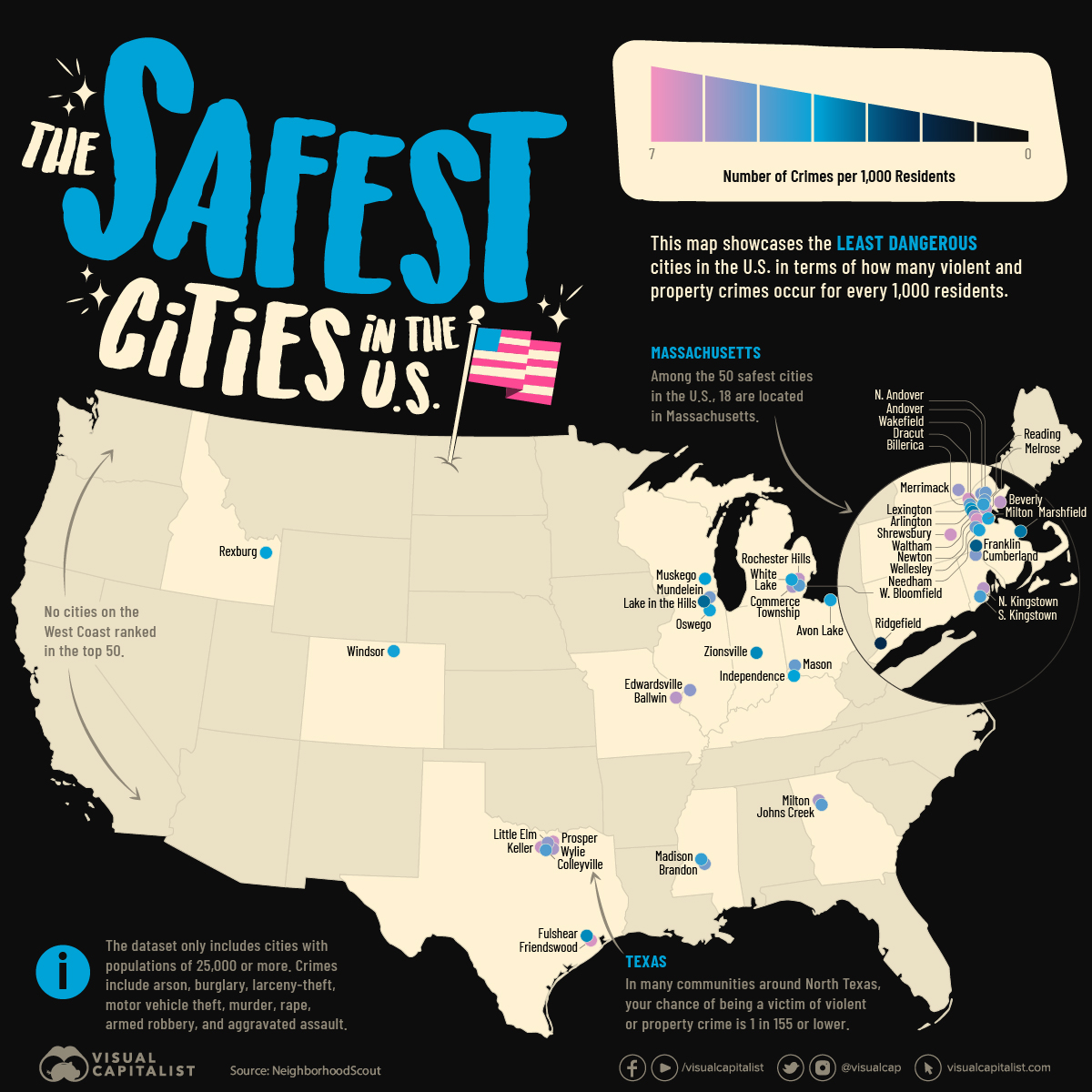
Mapped: The Safest Cities in the U.S.
How safe is small town America? This map reveals the safest cities in the U.S. in terms of the total crime rate per every 1,000 residents.
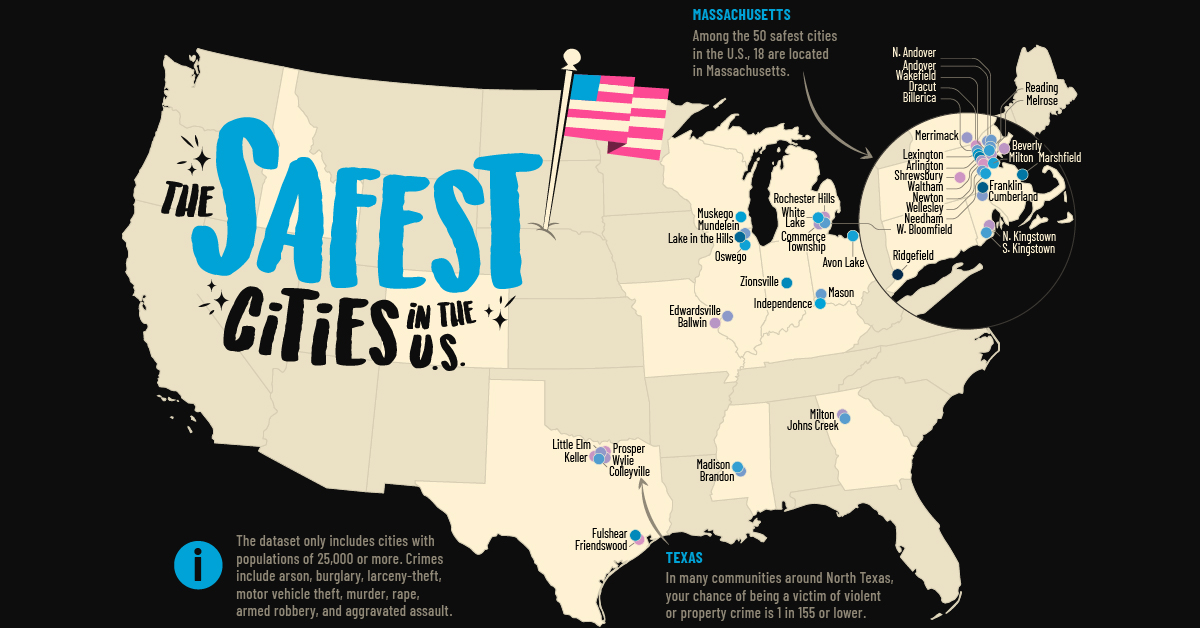
Mapped: The Safest Cities in America
The phrase “small town America” often conjures up images of white picket fences, well-trimmed lawns, and big houses. But how safe is modern-day suburbia in America?
Some of the smallest places in the country can actually be among the most dangerous. Take for example Bessemer, Alabama, with a population of around 26,000 and a violent crime rate of 33.1 per every 1,000 residents.
That said, there are many small cities that are true havens for families across the United States. This map showcases the safest cities in the U.S., using FBI data and Census Bureau populations compiled by NeighborhoodScout in 2023.
Note: The source only considered cities with a population of 25,000 or higher. This report is based on total index crimes reported in each city, which includes arson, burglary, larceny-theft, motor vehicle theft, murder, rape, armed robbery, and aggravated assault.
Top 100 Safest Cities in the U.S.
40% of the cities in the ranking are located in Northeastern states, which are typically rated the “safest” based on FBI data.
Here’s a closer look at the full list:
| Rank | City | State | Total Crime Rate(per 1,000 residents) | Chance of Beinga Victim |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ridgefield | Connecticut | 1.9 | 1 in 510 |
| 2 | Franklin | Massachusetts | 2.9 | 1 in 344 |
| 3 | Lake in the Hills | Illinois | 3.1 | 1 in 321 |
| 4 | Marshfield | Massachusetts | 3.3 | 1 in 300 |
| 5 | Arlington | Massachusetts | 3.4 | 1 in 292 |
| 6 | Fulshear | Texas | 3.6 | 1 in 276 |
| 7 | Zionsville | Indiana | 3.6 | 1 in 275 |
| 8 | Lexington | Massachusetts | 3.7 | 1 in 270 |
| 9 | Muskego | Wisconsin | 3.8 | 1 in 265 |
| 10 | Rexburg | Idaho | 3.9 | 1 in 253 |
| 11 | Independence | Kentucky | 3.9 | 1 in 253 |
| 12 | Oswego | Illinois | 4.1 | 1 in 238 |
| 13 | Milton | Massachusetts | 4.2 | 1 in 233 |
| 14 | Needham | Massachusetts | 4.2 | 1 in 233 |
| 15 | White Lake | Michigan | 4.2 | 1 in 233 |
| 16 | Avon Lake | Ohio | 4.3 | 1 in 232 |
| 17 | Madison | Mississippi | 4.5 | 1 in 221 |
| 18 | Wakefield | Massachusetts | 4.5 | 1 in 218 |
| 19 | Windsor | Colorado | 4.5 | 1 in 218 |
| 20 | South Kingstown | Rhode Island | 4.7 | 1 in 212 |
| 21 | Colleyville | Texas | 4.8 | 1 in 206 |
| 22 | West Bloomfield | Michigan | 4.9 | 1 in 204 |
| 23 | Johns Creek | Georgia | 4.9 | 1 in 202 |
| 24 | Billerica | Massachusetts | 5.1 | 1 in 195 |
| 25 | Mason | Ohio | 5.1 | 1 in 192 |
| 26 | Reading | Massachusetts | 5.1 | 1 in 192 |
| 27 | North Andover | Massachusetts | 5.2 | 1 in 190 |
| 28 | Wellesley | Massachusetts | 5.2 | 1 in 189 |
| 29 | Mundelein | Illinois | 5.3 | 1 in 187 |
| 30 | Brandon | Mississippi | 5.3 | 1 in 186 |
| 31 | Cumberland | Rhode Island | 5.4 | 1 in 184 |
| 32 | Andover | Massachusetts | 5.4 | 1 in 182 |
| 33 | Edwardsville | Illinois | 5.5 | 1 in 178 |
| 34 | Little Elm | Texas | 5.6 | 1 in 176 |
| 35 | Merrimack | New Hampshire | 5.7 | 1 in 172 |
| 36 | Waltham | Massachusetts | 5.8 | 1 in 169 |
| 37 | Wylie | Texas | 5.9 | 1 in 169 |
| 38 | Commerce Township | Michigan | 5.9 | 1 in 169 |
| 39 | Milton | Georgia | 5.9 | 1 in 167 |
| 40 | Melrose | Massachusetts | 6.0 | 1 in 164 |
| 41 | Ballwin | Missouri | 6.1 | 1 in 162 |
| 42 | North Kingstown | Rhode Island | 6.1 | 1 in 162 |
| 43 | Beverly | Massachusetts | 6.2 | 1 in 161 |
| 44 | Rochester Hills | Michigan | 6.2 | 1 in 160 |
| 45 | Keller | Texas | 6.3 | 1 in 158 |
| 46 | Shrewsbury | Massachusetts | 6.4 | 1 in 156 |
| 47 | Dracut | Massachusetts | 6.4 | 1 in 155 |
| 48 | Prosper | Texas | 6.4 | 1 in 155 |
| 49 | Newton | Massachusetts | 6.5 | 1 in 152 |
| 50 | Friendswood | Texas | 6.5 | 1 in 152 |
| 51 | McHenry | Illinois | 6.5 | 1 in 152 |
| 52 | Fort Mill | South Carolina | 6.6 | 1 in 151 |
| 53 | Wallingford | Connecticut | 6.8 | 1 in 146 |
| 54 | Caledonia | Wisconsin | 6.9 | 1 in 144 |
| 55 | Belmont | Massachusetts | 6.9 | 1 in 144 |
| 56 | De Pere | Wisconsin | 6.9 | 1 in 143 |
| 57 | Flower Mound | Texas | 7.0 | 1 in 142 |
| 58 | Easton | Massachusetts | 7.0 | 1 in 141 |
| 59 | Highland Park | Illinois | 7.0 | 1 in 141 |
| 60 | Carmel | Indiana | 7.2 | 1 in 138 |
| 61 | Sachse | Texas | 7.2 | 1 in 138 |
| 62 | Algonquin | Illinois | 7.2 | 1 in 137 |
| 63 | Hendersonville | Tennessee | 7.2 | 1 in 137 |
| 64 | San Luis | Arizona | 7.3 | 1 in 136 |
| 65 | Fishers | Indiana | 7.3 | 1 in 135 |
| 66 | Perrysburg | Ohio | 7.4 | 1 in 135 |
| 67 | Lake Stevens | Washington | 7.4 | 1 in 134 |
| 68 | Cheshire | Connecticut | 7.4 | 1 in 134 |
| 69 | Milford | Massachusetts | 7.5 | 1 in 132 |
| 70 | Saratoga Springs | Utah | 7.5 | 1 in 132 |
| 71 | Bella Vista | Arkansas | 7.5 | 1 in 132 |
| 72 | Princeton | New Jersey | 7.5 | 1 in 131 |
| 73 | Bluffton | South Carolina | 7.6 | 1 in 130 |
| 74 | Novi | Michigan | 7.6 | 1 in 130 |
| 75 | Chelmsford | Massachusetts | 7.6 | 1 in 130 |
| 76 | Amherst | Massachusetts | 7.7 | 1 in 129 |
| 77 | Rosemount | Minnesota | 7.7 | 1 in 129 |
| 78 | Gloucester | Massachusetts | 7.7 | 1 in 129 |
| 79 | Syracuse | Utah | 7.8 | 1 in 127 |
| 80 | Waukee | Iowa | 7.8 | 1 in 126 |
| 81 | Mequon | Wisconsin | 7.9 | 1 in 126 |
| 82 | Westfield | Indiana | 7.9 | 1 in 126 |
| 83 | Spring Hill | Tennessee | 7.9 | 1 in 126 |
| 84 | Upper Arlington | Ohio | 7.9 | 1 in 126 |
| 85 | Rahway | New Jersey | 7.9 | 1 in 125 |
| 86 | Montclair | New Jersey | 7.9 | 1 in 125 |
| 87 | Greenwich | Connecticut | 8.0 | 1 in 125 |
| 88 | Hutto | Texas | 8.0 | 1 in 124 |
| 89 | Vestavia Hills | Alabama | 8.0 | 1 in 123 |
| 90 | Brownsburg | Indiana | 8.1 | 1 in 123 |
| 91 | Wilmette | Illinois | 8.1 | 1 in 123 |
| 92 | New Milford | Connecticut | 8.1 | 1 in 122 |
| 93 | Hilliard | Ohio | 8.2 | 1 in 120 |
| 94 | Royal Oak | Michigan | 8.2 | 1 in 120 |
| 95 | Derry | New Hampshire | 8.3 | 1 in 121 |
| 96 | Dublin | Ohio | 8.3 | 1 in 120 |
| 97 | West Warwick | Rhode Island | 8.5 | 1 in 116 |
| 98 | Watertown | Massachusetts | 8.5 | 1 in 116 |
| 99 | Walpole | Massachusetts | 8.6 | 1 in 115 |
| 100 | Kaysville | Utah | 8.6 | 1 in 115 |
One quarter of the safest cities are located in Massachusetts, with the vast majority clustered around Boston.
The median population of the cities and towns in the top 100 is just 32,000, and few widely-recognized cities make the list. Carmel, Indiana (#60) is the only city with a population above 100,000 to make the rankings. This would seem to follow the logic that bigger cities are more dangerous, but our map covering the most dangerous cities in America shows that many small cities were just as dangerous, and some even more.
Regardless, small towns can truly be idyllic. For example, a person’s chance of falling victim to crime in Ridgefield, Connecticut, the safest ranked city in the U.S., is just 1-in-510. That’s an overall rate of fewer than two incidents of crime per every 1,000 residents.
One surprising observation from the data is that many of the safest U.S. cities are in very close proximity to some of the most dangerous.
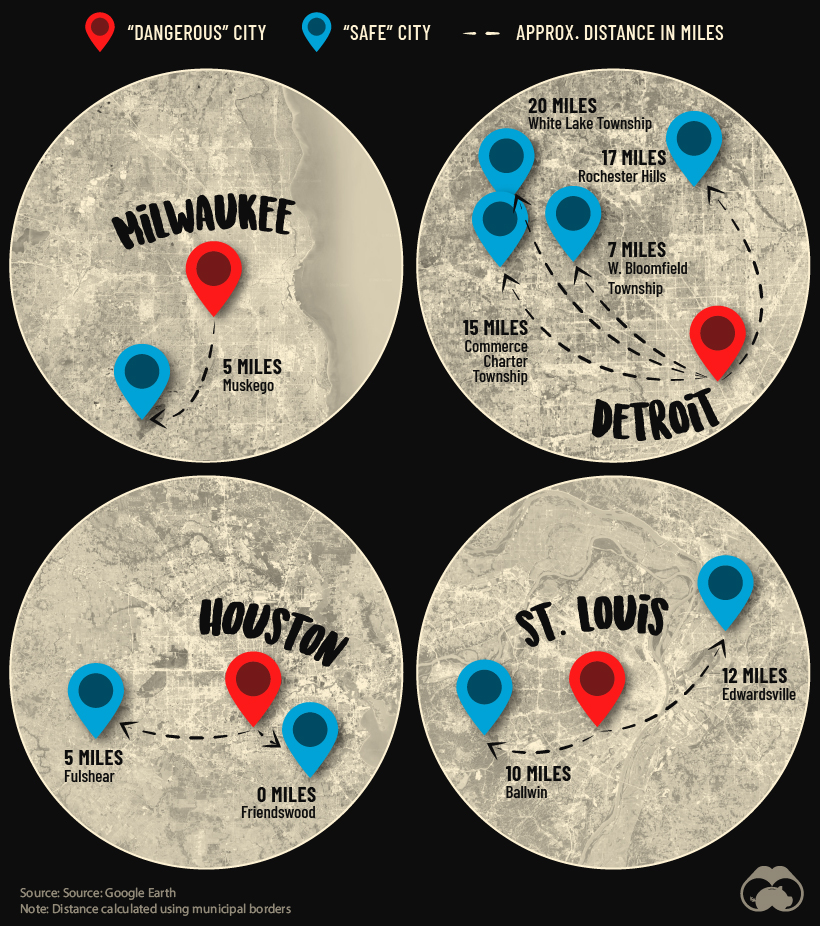
One example that illustrates this is Detroit, which ranks as the sixth most dangerous city in America. Despite this, as shown on the map above, there are four communities nearby that have some of the lowest crime rates in America.
In other words, America’s metro areas contain much contrast, and these insights provide valuable information for individuals and families seeking secure places to live across the country.
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoVisualizing 1 Billion Square Feet of Empty Office Space
-
 Energy4 weeks ago
Energy4 weeks agoLife Cycle Emissions: EVs vs. Combustion Engine Vehicles
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoVintage Viz: The World’s Rivers and Lakes, Organized Neatly
-
 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoVisualized: The 100 Largest U.S. Banks by Consolidated Assets
-
 Automation1 week ago
Automation1 week agoCharted: Changing Sentiments Towards AI in the Workplace
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoWhat are Top Investment Managers Holding in Their Portfolios?
-
 Stocks1 week ago
Stocks1 week agoThe 50 Best One-Year Returns on the S&P 500 (1980-2022)
-

 Markets3 weeks ago
Markets3 weeks agoChart: U.S. Home Price Growth Over 50 Years